Electric bikes, or e-bikes as they are sometimes called, provide users with an easy way to zoom over terrain and enjoy some fresh air and exercise. I, for one, love the feeling of freedom that comes when riding a bike, and even though e-bikes do make for easier riding, that doesn’t mean you can’t get some great exercise every time you ride.
Of course, one of the main reasons why many people choose electric bikes is because they are a good form of transportation for their positive impact on the environment.
E-bikes can help you achieve a reduction in your carbon footprint and it is a form of transportation that does not release dangerous chemicals into the air like a car or bus. The batteries are easily recycled and their health benefits place even less burden on the health-care system.
Cars Versus E-Bikes
When you look at the facts, there is no denying that when you compare e-bikes to cars and other vehicles, e-bikes win by a landslide. Indeed, when comparing any type of bicycle to cars and busses, the bike always wins in terms of energy and environmental impact.
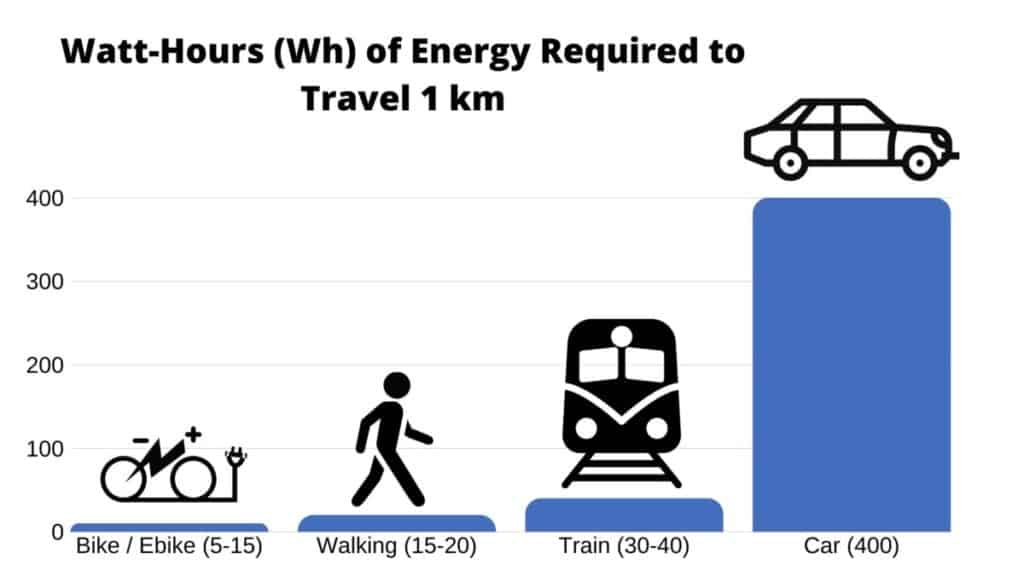
For example, to travel just one kilometer, a standard bike uses 5-15 watt-hours (w-h) of energy, as compared to 15-20 w-h by foot, 30-40 by train, and a whopping 400 w-h in an average-sized car with one person.
Comparing Calories
The average e-bike rider will likely consume more calories than people who take their car or a bus to and from work, which increases the amount of carbon dioxide emitted each day, month, and year. And let’s face it, carbon dioxide is no friend to the environment. But is this extra amount of carbon dioxide enough to make it worth it to scrap the idea of riding an e-bike altogether? Most experts don’t think so.
In fact, most studies done on e-bikes have come to the same conclusion – that riding e-bikes is in fact better for the environment even after you take everything else into consideration, simply because e-bikes provide numerous advantages over using other forms of transportation.
Is Less Energy Really Used with an E-Bike Compared to a Standard Bicycle?
When comparing an e-bike with a regular bike, most would think that riding with muscle power alone would be the greener way by far. There’s no battery, less weight and you don’t need to charge up from a power grid that generates power from any number of sources (green or otherwise).
However, surprisingly, riding an electric bike can actually use less energy and have less impact on the environment than riding a regular bike.
How?
One of the factors taken into consideration when comparing how good e-bikes are for the environment versus traditional bikes is food consumption.
The average human-powered bike rider with a daily commute of 30 miles will likely consume an additional 800 calories each day, this alone is going to increase the amount of carbon dioxide emitted into the air every day through the energy needed to produce, package, transport and prepare these extra calories of food each day.
Propelling a bike, whether an electric bike or human-powered will take about the same 5-15 wh per km. Just comparing the efficiency and the source of the energy required to provide that power is what can be deceiving between electric bikes and human-powered bikes.
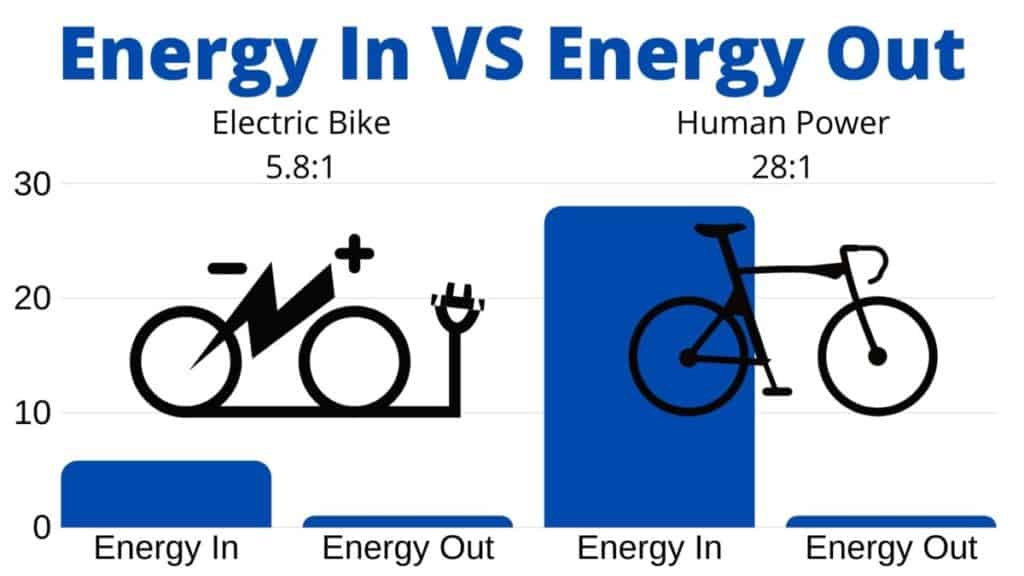
This white paper compared ebikes and human-powered bikes and the energy inputs and outputs required for each system. The paper found that “on average each unit of mechanical energy that a cyclist delivers to the pedals comes at the expense of 28 units of primary energy (i.e. Fossil fuels).”, or a ratio of 1:28.
This compares to the energy ratio for an ebike with a lithium-ion battery to be around 1:5.8. This scenario compares typical food production energy ratios and average power grid efficiency and energy ratios.
The energy scales between ebikes and human-powered bikes get even better for both modes and can be balanced more by using more locally sourced materials. That is more locally sourced materials for ebikes and more locally-grown food for human-powered bikes.
In these more ideal conditions, this ends up with both types of bikes having similar energy consumption characteristics (1:3 to 1:4 ratio) – meaning for every Giga-Joule of energy output as the movement of the bike/ebike, 3-4 Giga-Joules of energy is required as input.
In the end they are both very efficient and miles ahead of cars in this respect.
How to Get Rid of an E-Bike Battery
One of the concerns some people have regarding the “green” effects of an e-bike is the battery that is needed to operate the bike. Specifically, concerns center around what to do with the battery once it’s no longer being used. Let’s face it, no one wants to see any type of bike or car battery go into landfills, because dangerous chemicals could leach out into the soil, which is unsafe to say the least.

Since e-bikes are relatively new, you may wonder what you should do with your battery once you decide you no longer need it. Fortunately, putting it in a landfill doesn’t have to be your only option. In fact, in countries like the United States and others, more and more facilities are cropping up that will take your e-bike battery and recycle it, and this is more valuable than you might think.
The lithium-ion batteries commonly used in e-bikes are the easiest to recycle because lithium is used a lot in manufacturing products such as laptops and cell phones. Even though it is currently cheaper to mine lithium than to extract it from recycled products such as e-bike batteries, this is very likely to change in the near future, especially if e-bikes continue to grow in popularity like they have thus far.
NiCad batteries are a bit more complicated, in part because no type of cadmium battery is allowed in landfills. Because of this, it is often more of a challenge to dispose of your NiCad e-bike battery, but all is not lost. Just like lithium-ion batteries, NiCad batteries can be recycled, and all it takes is a little effort on your part to find a facility that can accommodate this need.
Disposal of lithium-ion or NiCad rechargeable batteries in the United States can be handled by CALL2RECYCLE or call at (877) 723-1297.
How Much of a Carbon Footprint Does an E-Bike Leave Behind?
The popularity of electric bikes is here to stay because let’s face it, the world is not going backwards when it comes to finding ways to better reduce our carbon footprint. Your carbon footprint is affected by many of your actions, including what you use to power your home, what you eat, and of course, how you get from Point A to Point B day after day.
The goal, of course, is to reduce our carbon footprint in as many ways as possible, so any time you can hop on an e-bike instead of getting behind the wheel of a car, you’re doing your part to reduce your carbon footprint. E-bikes don’t use gas and therefore don’t spew dangerous chemicals and smoke into the air each time you ride, making them a very eco-friendly way to help the environment.
According to a study conducted by the European Cyclists Federation, e-bikes are even better for the environment than electric cars, creating 2.5 to 5 grams of carbon dioxide per mile as compared to 150 grams per mile for an electric car. And when you compare that number to gas- or diesel-powered vehicles or busses, there is an even bigger difference in those numbers.
Consider the Source of Electricity for Charging Your Ebike
Producing the electricity needed to operate an e-bike can involve “dirty” coal, so is this really a good alternative to taking busses and driving cars? Yes, according to experts. The average e-bike requires only about 10% of the energy needed to operate a standard car, and it is six times more efficient than using rail transit.
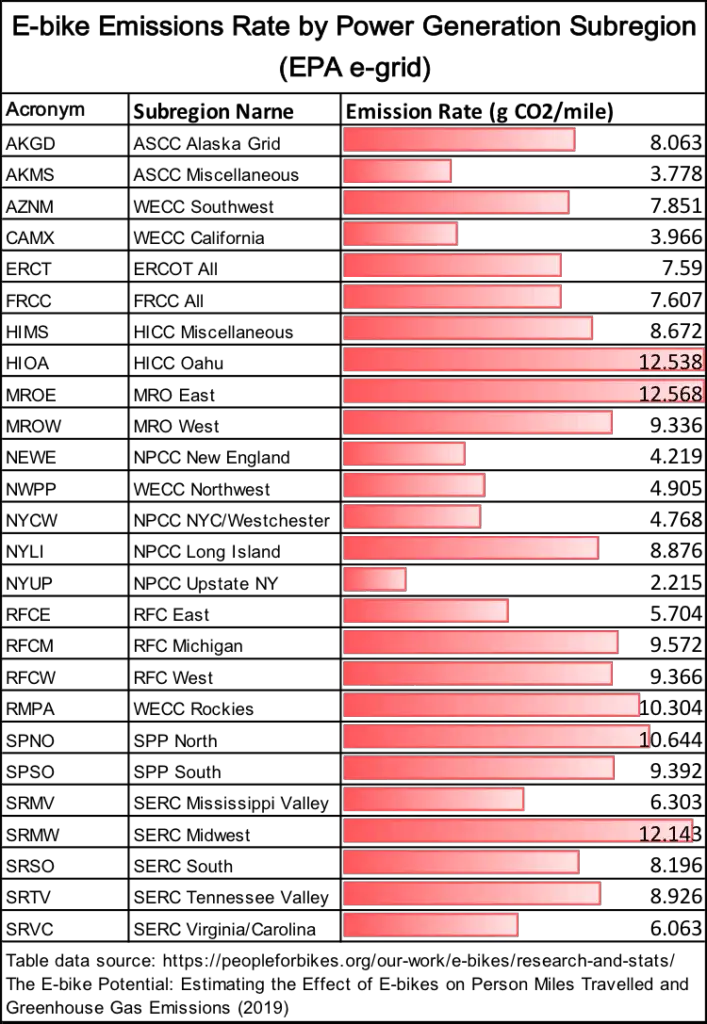
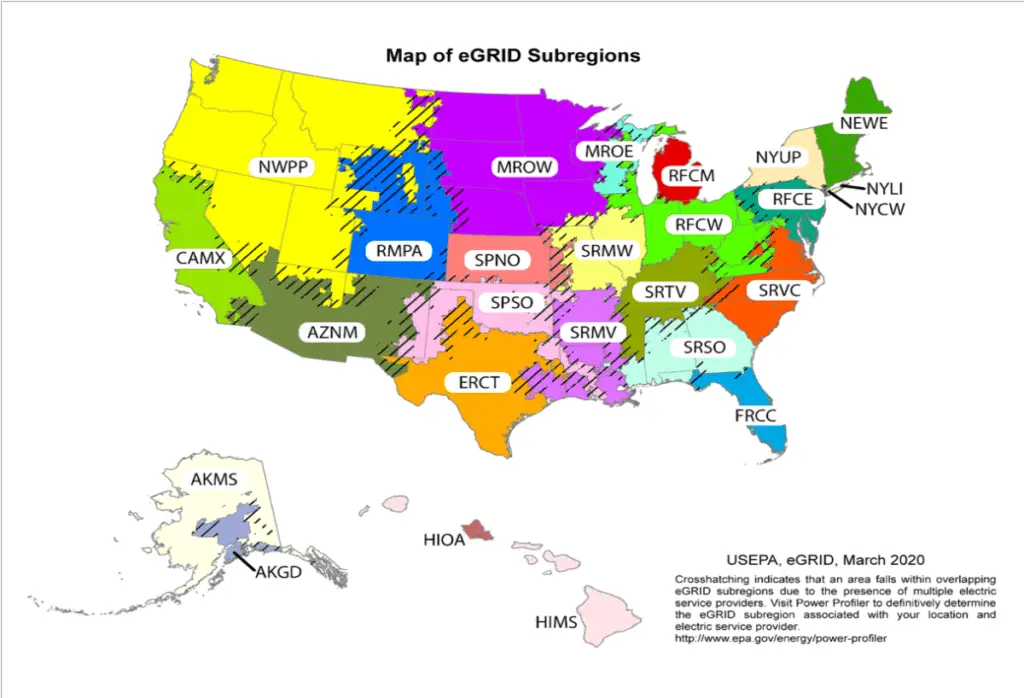
Although the amount of electricity you’ll need to charge an electric bike battery may be small, when charging with green or less polluting power, your environmental impact will be less. Here’s a list of several regions in the US and the average grams of CO2 emitted per mile of ebike riding. Areas with more efficient power and hydro-electric power result in an overall lower CO2 emitted per mile of ebike riding.
And in case you don’t know where all these regions are, here’s the map that goes along with the table above.
What About Human Benefits?
E-bikes also offer numerous “human” benefits, and it is not difficult to figure out what these are. For starters, riding an e-bike is a lot healthier for you than driving an automobile and can result in monthly fees and costs that are a lot lower. Let’s face it, the money you spend on gas, insurance, and parking fees alone can be quite high, but with e-bikes, none of these expenses are necessary.
Everyone knows that with regular exercise, people can feel better both physically and psychologically for a lifetime, and even if you have stiff joints or sore muscles, riding an e-bike is much easier on you than running or other high-impact aerobic activity. In fact, even people who are suffering from conditions such as arthritis often find that riding an e-bike provides them with great cardiovascular activity without the jarring on the joints that are prevalent in other types of activity.
In addition, the more people are outside in the sunshine, the greater their intake of vitamin D, since the two must work together to be efficient. Many people today are lacking in vitamin D, not because the vitamin isn’t present in their system, but because they don’t get enough sunshine to make the vitamin work the way it’s supposed to.
Getting lots of sunshine each day is important for a lot of reasons, and if you’re going to be outside anyway, why not make the most of it and get some exercise by riding your e-bike? Just like riding a regular bicycle, riding an e-bike is a great way to get the exercise you need and the sunshine you enjoy, and they are just challenging enough to get a good workout in without being too difficult to ride.
E-bikes also provide practical solutions to some of today’s most pressing problems. If the number of people riding bikes instead of driving cars increased by just 10%, for example, we’d have a much healthier society, which could very well result in lower healthcare costs for everyone. This is but one of the many examples of why e-bikes are such a great addition to other modes of transportation.
The Bottom Line: The Advantages of an E-Bike
So, we’ve already determined that riding an e-bike is great for the environment and that your carbon footprint when using an e-bike is roughly equivalent to that of using a standard bicycle, but is this the only way that an electric bike can help the environment? No, because there are many other ways it can do so.
First of all, more than 30% of carbon dioxide, 80% of carbon monoxide, and 50% of nitrogen oxide emissions every year are produced by motor vehicles. And to make it worse, many of these vehicles are driven by people who are commuting very short distances from their home each day. Because of this, if every American who drives five miles or less to work were to switch to an electric bike just one day a week, it would have the same effect as taking one million cars off the road immediately.
Driving cars results in huge amounts of fossil fuel usage and harmful emissions, which doesn’t happen if you ride an e-bike instead. Yes, there is the manufacturing process involved in creating new e-bikes, which can be considered a strain on the environment, but this is minimal and is nothing compared to the manufacturing of regular motor vehicles.
Other ways e-bikes can help improve the environment include the following:
- They are sustainable and use no fossil fuels
- They result in little to no harmful emissions
- They don’t damage the roadways like cars often do
- They can reduce the amount of congestion on highways
- They are lower in cost to utilize and maintain